NRI income received outside of India is not taxed in India by default. However, if an NRI’s income in India exceeds the basic exemption ceiling as stated by the Income Tax Act, such as capital gains from investments in shares, mutual funds, property rental, and term deposits, the NRI must submit a tax return.
It’s critical to comprehend how an NRI becomes obligated to pay taxes in India. According to FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act) criteria, a citizen of Indian origin may only be classified as an NRI if he or she has spent a certain number of days abroad and therefore has maintained a relative time of absence from India.
NRI Income Tax Rules: Income from Salary
Your income from salary is taxable in India under the following two circumstances:
- If received in India: If you have received the salary in your Indian Bank Account or someone else has received it on your behalf, it would be taxable in India.
- If earned in India: If you have received your salary in lieu of the services rendered in India, it would be taxable in India no matter whether you receive it in India or abroad.
NRI Income Tax Rules: Rent from House Property
If you have a house property in India and receive rental income from the same, it would be taxable. The taxable income would be calculated in a similar manner as applicable to a resident Indian
NRIs, as well as residents, are allowed the following deductions from the rental income:
- Standard dedu ction @ 30%
- Municipal and property taxes, paid
- Interest deduction on home loan u/s 24b
- Principal repayment of home loan upto Rs. 1.50 Lakhs, u/s 80C.
Your tenant must credit the rent in your NRO account and deduct a 30% TDS on the rent before making the payment.
NRI Income Tax Rules: Income from Capital Gains on Real Estate
If you have sold any property in India then you are liable to pay taxes on the gains. The rules for income tax for NRI in India with respect to capital gains on real estate are the same as that of Indian residents.
You are also allowed the exemptions u/s 54, and 54F by buying another house property 1 year before or within 2 years of selling the property or by constructing a house property within 3 years.
Alternatively, you can also invest in the capital gain bonds u/s 54EC within 6 months of the date of sale.
However, the only difference is that long-term capital gains on real estate for NRIs are subject to a TDS of 20% and short-term gains are subject to a TDS of 30%.
Capital Gains on Financial Assets
If you have booked any gains on investments in equity shares or mutual funds in India, these would be taxable.
In Listed Equity Shares and Equity Mutual funds, gains booked after 12 months of holding period are considered as Long term Capital Gains, which beyond Rs.1 Lakh would be taxed at 10%, without indexation.
If sold within 12 months, the gains would be treated as short-term and taxed at 15%.
Gains on listed non-equity funds, if sold after a period of 36 months, would be treated as long-term and taxed at 20% with indexation, and non-listed funds at 10% without indexation.
If sold within 36 months, the gains would be treated as short-term and taxed as per the income tax slabs applicable.
As per the rules for Income Tax for NRI in India, you can take the benefit of indexation only on listed non-equity instruments, not on the unlisted funds. Please note that all open-ended non-equity Mutual funds are Unlisted in nature.
However, the TDS applicable on the short-term capital gains on non-equity funds would be 30%.
Tax Returns for NRIs
As explained in the section above, the taxable income of an NRI will not necessarily include certain incomes from investments and long term capital gains. Those aspects of income have tax deducted at sources. In case there are sources of income apart from the prior mentioned sources, they would need to be declared and would be taxable as per the prevailing tax rules.
However, in certain cases, the TDS incurred on income from investment and long term capital gains amounts to more than the tax liability of the individual. To have a tax refund or claim an exemption, filing of tax return becomes necessary.
NRIs can visit the online portal of Income Tax Department of India to file their tax returns and it is a preferred way of filing tax returns.
NRI Income Tax Rules: Income from Other Sources
Interest:
The interest on NRO Accounts and Fixed Deposits is taxable if exceeds Rs.10,000 in a financial year. The interest income on the NRE and FCNR deposits is fully tax-free.
Dividend:
If you receive any dividend from any Indian company or mutual funds exceeding Rs. 5,000 in a financial year, it would be taxed at 20%.
However, this rate can be even lower if the provisions of DTAA are available. This is due to the fact that the tax treaties with most of the countries limit the taxation on dividends between 5% to 15%.
Gifts:
Gifts received from relatives as defined in the income tax act are exempt from taxes. Gifts received from non-relatives beyond Rs. 50,000 in a financial year are fully taxable. However, gifts received on the occasion of marriage are fully tax-exempt.
Income from Salary, House Property, and Other Sources in India would be added to the total income and taxed as per the income tax slab rates applicable.
Tax Exemptions for NRIs
- Interest earned on NRE/FCNR accounts
- Interest earned on government issued savings certificates and notified bonds
- Dividends earned from shares of domestic Indian companies
- Long term capital gains from listed equity shares and equity-oriented mutual funds
- Capital gains can be exempted through the sections and conditions as-
- Section 54 – In case a house property held for 3 or more years is sold and the proceeds or part thereof are used to purchase another property or deposited in a PSU or other banks as per the Capital Gains Account Scheme of 1988
- Section 54F – In case any property other than a house is sold and capital gains are incurred, this exemption can be claimed on the construction or purchase of a new house in proportion to how much of the sale proceeds have been spent on the new asset
- Section 54EC – If long term capital gains are invested in bonds like the ones issued by the National Highway Authority of India and Rural Electrification Corporation. These have a redemption value after 3 years and shouldn’t be sold before that. In such cases, as per the budget of 2014, a maximum of INR 50 lakhs can be invested in a financial year
All the above exemptions are subject to the tax laws prevalent at that time.
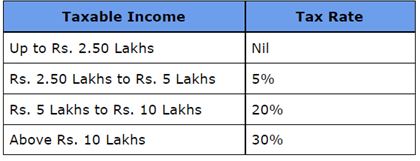
NRI Income Tax Slabs:
The tax slabs applicable to NRIs are as below. These slabs are applicable to all NRIs, irrespective of their age. In other words, unlike resident Indians, even if you are a senior citizen NRI, the basic exempt income is Rs. 2.50 Lakhs only.
Old Tax Regime:
New Tax Regime:
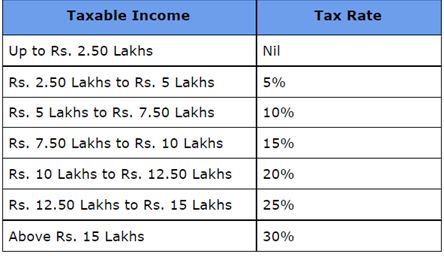
Rebate u/s 87A is not available for NRIs. It means that even if your income in India is below Rs. 5 Lakhs, you need to pay the taxes, as applicable.
In addition, a cess of 4% on the taxes is also applicable. And, if your income is above Rs. 50 Lakhs, a surcharge will also be applicable on the total tax payable.
Please note that, the basic exemption limit of Rs. 2.50 Lakhs is not available if your total income consists of short & long-term capital gains only.

